The state oil company Pemex released some 40,000 tonnes of methane into the atmosphere from a Gulf of Mexico oil and gas platform last December, according to a study by a team of European scientists.
The European Space Agency (ESA) announced the results of the study on Thursday.
“A team of scientists have used satellite data to detect methane plumes from an offshore platform in the Gulf of Mexico,” the ESA said. “This is the first time that individual methane plumes from offshore platforms are mapped from space,” it added.
Methane, the main constituent of natural gas, is much more harmful to the environment than carbon dioxide and is considered a major contributor to global warming.
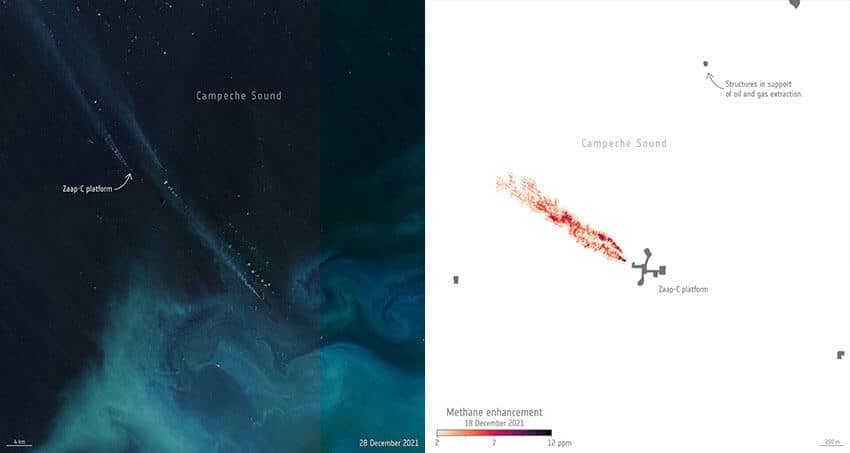
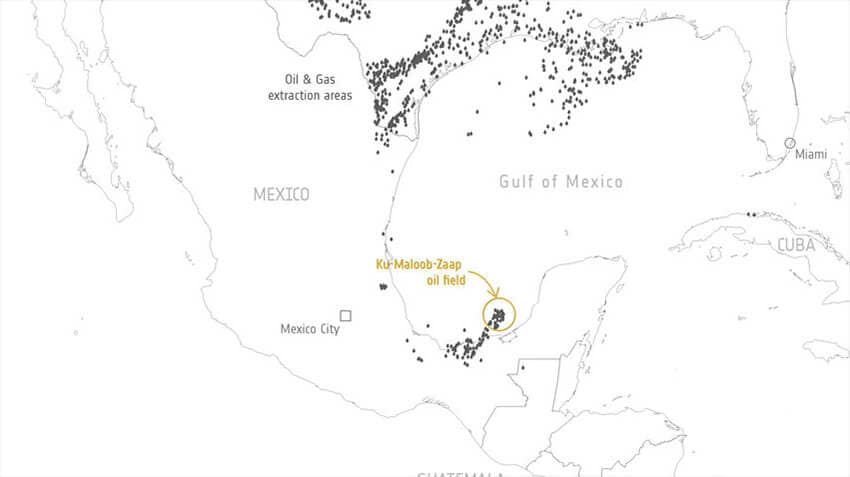
The ESA said that a team led by scientists from Spain’s Valencia Polytechnic University (UPV) used satellite data “to detect and quantify strong methane plumes from an offshore oil and gas production platform near the coast of Campeche in one of Mexico’s major oil producing fields.”
“… The team found that the [Zaap-C] platform released high volumes of methane during a 17-day ultra-emission event which amounted to approximately 40,000 tonnes of methane released into the atmosphere in December 2021,” the agency said.
“These emissions are equivalent to around 3% of Mexico’s annual oil and gas emissions and this single event would have a similar magnitude to the entire regional annual emissions from Mexico’s offshore region. … The results from this analysis showed that this ultra-emitting event, likely related to abnormal process conditions, was a one-time incident with the longest duration since flaring activity began at this platform,” the ESA said.
Luis Guanter, a UPV researcher who co-authored the study, said the results “demonstrate how satellites can detect methane plumes from offshore infrastructure.”
“This represents a breakthrough in the monitoring of industrial methane emissions from space, as it opens the door to systematic monitoring of emissions from individual offshore platforms,” he said.
Itziar Irakulis-Loitxate, a UPV scientist and the study’s lead author, said that she and her colleagues are in fact expanding their analysis to other offshore oil and gas production regions.
The news agency Reuters sought comment from Pemex and the federal Energy Ministry about the study’s findings but didn’t receive a response from either.
Mexico News Daily
